원래 HITCON Training Lab11 문제풀이를 정리하려고 했는데, 내 서버 환경의 GLIBC 버전이 2.31이어서 다 막혔다. 그래서 그냥 내가 이해할 수 있게 공격기법만 정리하고 나중에 실습할 수 있는 다른 문제를 풀어볼 예정이다.
Lab11
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
struct item{
int size ;
char *name ;
};
struct item itemlist[100] = {0};
int num ;
void hello_message(){
puts("There is a box with magic");
puts("what do you want to do in the box");
}
void goodbye_message(){
puts("See you next time");
puts("Thanks you");
}
struct box{
void (*hello_message)();
void (*goodbye_message)();
};
void menu(){
puts("----------------------------");
puts("Bamboobox Menu");
puts("----------------------------");
puts("1.show the items in the box");
puts("2.add a new item");
puts("3.change the item in the box");
puts("4.remove the item in the box");
puts("5.exit");
puts("----------------------------");
printf("Your choice:");
}
void show_item(){
int i ;
if(!num){
puts("No item in the box");
}else{
for(i = 0 ; i < 100; i++){
if(itemlist[i].name){
printf("%d : %s",i,itemlist[i].name);
}
}
puts("");
}
}
int add_item(){
char sizebuf[8] ;
int length ;
int i ;
int size ;
if(num < 100){
printf("Please enter the length of item name:");
read(0,sizebuf,8);
length = atoi(sizebuf);
if(length == 0){
puts("invaild length");
return 0;
}
for(i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++){
if(!itemlist[i].name){
itemlist[i].size = length ;
itemlist[i].name = (char*)malloc(length);
printf("Please enter the name of item:");
size = read(0,itemlist[i].name,length);
itemlist[i].name[size] = '\x00';
num++;
break;
}
}
}else{
puts("the box is full");
}
return 0;
}
void change_item(){
char indexbuf[8] ;
char lengthbuf[8];
int length ;
int index ;
int readsize ;
if(!num){
puts("No item in the box");
}else{
printf("Please enter the index of item:");
read(0,indexbuf,8);
index = atoi(indexbuf);
if(itemlist[index].name){
printf("Please enter the length of item name:");
read(0,lengthbuf,8);
length = atoi(lengthbuf);
printf("Please enter the new name of the item:");
readsize = read(0,itemlist[index].name,length);
*(itemlist[index].name + readsize) = '\x00';
}else{
puts("invaild index");
}
}
}
void remove_item(){
char indexbuf[8] ;
int index ;
if(!num){
puts("No item in the box");
}else{
printf("Please enter the index of item:");
read(0,indexbuf,8);
index = atoi(indexbuf);
if(itemlist[index].name){
free(itemlist[index].name);
itemlist[index].name = 0 ;
itemlist[index].size = 0 ;
puts("remove successful!!");
num-- ;
}else{
puts("invaild index");
}
}
}
void magic(){
int fd ;
char buffer[100];
fd = open("/home/bamboobox/flag",O_RDONLY);
read(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
close(fd);
printf("%s",buffer);
exit(0);
}
int main(){
char choicebuf[8];
int choice;
struct box *bamboo ;
setvbuf(stdout,0,2,0);
setvbuf(stdin,0,2,0);
bamboo = malloc(sizeof(struct box));
bamboo->hello_message = hello_message;
bamboo->goodbye_message = goodbye_message ;
bamboo->hello_message();
while(1){
menu();
read(0,choicebuf,8);
choice = atoi(choicebuf);
switch(choice){
case 1:
show_item();
break;
case 2:
add_item();
break;
case 3:
change_item();
break;
case 4:
remove_item();
break;
case 5:
bamboo->goodbye_message();
exit(0);
break;
default:
puts("invaild choice!!!");
break;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
기능은 show, add, change, remove, exit 5가지가 있다. add, change, remove를 통해 item 구조체를 관리할 수 있다. 이때, box 구조체의 bamboo가 가장 처음으로 힙 메모리에 할당된다. 아래는 bamboo와 2개의 item 구조체를 add를 한 모습이다.
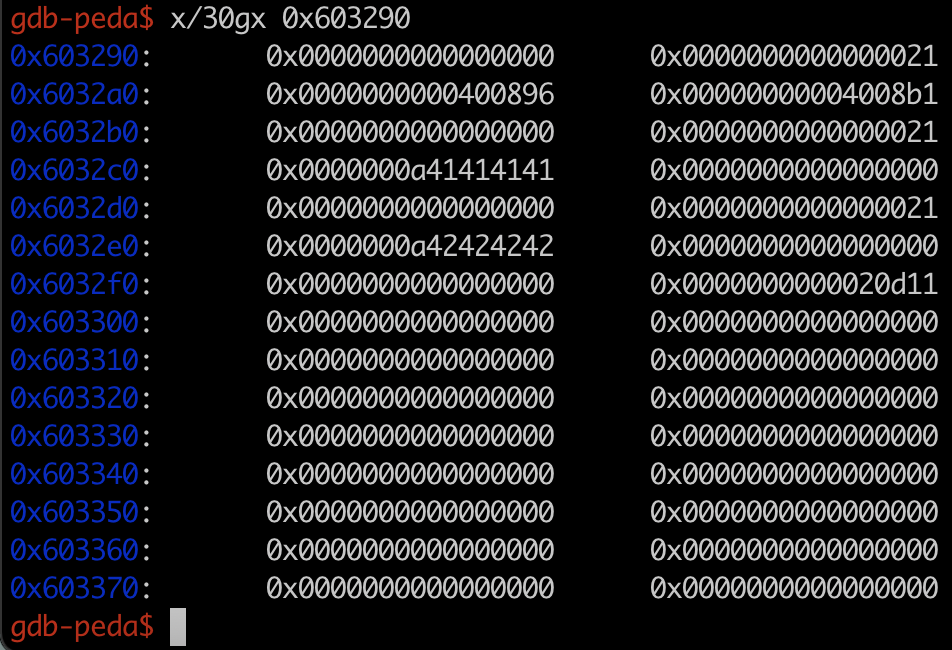
0x6032a0, a8에는 hello_message, goodbye_message의 함수 주소가 박히고 아래는 각각 item 구조체의 힙 구조다. hello_message 함수는 프로그램이 처음 시작할 때, 실행되고, 종료될 때는 bamboo->goodbye_message( )가 실행된다. 따라서 bamboo->goodbye_message( )가 있는 0x6032a8을 magic 함수로 덮어써서 문제를 해결하면 될 것 같다.
House of Force
위의 사진에서 0x6032f0을 보면 해당 주소가 Top chunk이다. 만약 프로그램에서 malloc을 하고 요청한 사이즈를 처리할 수 있는 bin list가 없다면, Top chunk의 공간을 사용한다. 이때, Top chunk의 size를 0xffffffffffffffff로 변조하고, 다음과 같은 크기로 malloc을 요청하면 원하는 주소에 값을 쓸 수 있다.
[원하는 주소] - [Chunk Header Size (0x10 or 0x8)] - [Top Chunk Addr] - [Chunk Header Size (0x10 or 0x8)]
https://www.lazenca.net/display/TEC/The House of Force
해당 문제에서는 add_item( )을 통해 할당하고, change_item( )을 이용하여 Top chunk의 size를 덮어쓸 수 있다. 탑청크의 사이즈까지는 변조했지만 다음 코드에 의해 막히고 다른 문제풀이를 보니깐 Unsafe Unlink로도 풀 수 있다고 해서 그 공격 기법도 알아봤다.
victim = av->top;
size = chunksize (victim);
if (__glibc_unlikely (size > av->system_mem))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): corrupted top size");
Unlink
Unlink는 이미 있는 bin list의 chunk가 double-linked list로 구성되어있는데, 이때 구조의 변화가 생기며 이를 수정해야할 때, fd와 bk를 변경하는 과정을 의미한다. (BK <--> P <--> FD에서 BK <--> FD로 수정하는 과정을 의미.)
/* Take a chunk off a bin list */
#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) {
if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0))
malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted size vs. prev_size", P, AV);
FD = P->fd;
BK = P->bk;
if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0))
malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV);
else {
FD->bk = BK;
BK->fd = FD;
if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (P))
//(https://www.lazenca.net/display/TEC/Unsafe+unlink)코드를 보면, 첫 번째 if문에서 P의 size와 P의 다음 청크의 크기가 같은지 비교한다. 두 번째 if문에서는 FD->bk와 BK->fd가 P인지 비교한다. (FD->bk와 BK-fd가 해제할 포인터인지 비교)
Unsafe Unlink
Unsafe Unlink는 Unlink의 과정을 악용하여 공격하는 기법이다. 공격흐름은 다음과 같다.
- 2개의 chunk를 할당한다.
- 첫 번째 chunk 안에 Fake chunk를 생성한다. 이때, 두 번째 chunk의 prev_size와 size를 덮을 수 있어야 한다.
- Fake Chunk의 구조
- prev_size, size: 0x0
- fd: [원하는 주소] - 24, bk: [원하는 주소] - 16
- 두 번째 chunk의 prev_size 수정 , size: PREV_INUSE flag 제거 (fake chunk가 free 된 것으로 인식)
- 두 번째 chunk를 해제한다.
- free 과정을 진행하며, PRV_INUSE flag가 0이므로 이전 chunk가 free 된 것으로 인식하고 prev_size를 통해 fake chunk와 unlink 과정 수행
- 첫 번째 if문 우회
- chunksize(fake_chunk) = 0, prev_size(next_chunk(fake_chunk)) = 0
- 다음 chunk의 size를 구할 때, fake chunk의 size를 더해 다음 size를 구하는 걸로 기억하는데 0이므로 자기 자신을 가리키는 걸로 기억함.
- 두 번째 if문 우회
- 만약 원하는 주소를 0x1234라고 가정.
- FD = P->fd, BK = P->bk
- FD->bk = P->fd->bk, P->fd = 0x1234-24, 0x1234-24 -> bk이면 bk가 0x1234로부터 +24 위치에 있으므로 0x1234임.
- BK->fd = P->bk->fd, P->bk = 0x1234-16, 0x1234-16 -> fd이면 fd가 0x1234로부터 +16 위치에 있으므로 0x1234임.
- unlink 수행
- 0x1234 주소에 [0x1234 - 24] 값이 존재할 것이다.
- 이를 이용해서 공격을 수행
lab11 문제의 경우, itemlist에 size와 name 포인터가 저장된다. itemlist+8의 위치에는 인덱스 0의 name ptr이 저장된다. 위의 fake chunk를 구성할 때, fd와 bk를 [0x6020c8 - 24], [0x6020c8 - 16]으로 설정한다. (0x6020c8 = itemlist+8) 그리고 unlink가 진행된다면, itemlist+8의 위치에 0x6020b0(=0x6020c8 - 24)값이 저장된다. 그리고 change_item을 이용해 0번 인덱스를 수정하면 0x6020b0주소부터 수정할 수 있다. 원하는 함수 got로 itemlist+8을 덮어쓰고 공격을 진행하면 될 것 같다.
'Security' 카테고리의 다른 글
| HITCON Training Lab13 (0) | 2021.01.02 |
|---|---|
| HITCON Training lab12 (0) | 2020.12.31 |
| HITCON Training lab10 (first fit, uaf) (0) | 2020.12.22 |
| HITCON Training lab7 ~ 9 (0) | 2020.11.21 |
| BOF 중 scanf에 대한 글 (0) | 2020.11.13 |



